THE IMMUNOPHENOTYPIC CHARACTERISTICS OF CD19 POSITIVE MYELOMA AND ITS PROGNOSTIC IMPACT
(Abstract release date: 05/21/15)
EHA Library. Mya H. 06/12/15; 102908; PB1872
Disclosure(s): Hospital Universitario de SalamancaHaematology

Hae Tha Mya
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB1872
Type: Publication Only
Background
Clonal plasma cells (CPCs) in multiple myeloma were usually characterized by negative CD19 expression by multiparametric flow cytometry (MFC). However, positive CD19 expression in CPCs was noted in some cases with the reported incidence ranging from 0 to 8%. Positive CD19 expression in CPCs could complicate the minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment by high sensitivity MFC as the majority of polyclonal plasma cells (PPCs) retained CD19 expression. In addition, CD19 positive myeloma patients were reported to have a poorer clinical outcome in the group of patients treated with induction chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation.
Aims
We aimed to review the immunophenotypic features of CD19 positive myeloma patients in comparison with that of CD19 negative cases to determine specific immunophenotypes which could be useful for MRD assessment. The prognostic impact of positive CD19 expression on clinical outcome in patients treated with the regimens including novel therapies was also evaluated.
Methods
A retrospective review of newly diagnosed myeloma patients in a single centre was performed for the period of Jan 2006 to Jan 2015. The clinical data was retrieved from the patient information system of the institution as well as by reviewing the clinical records. Multiparametric flow cytometry analysis was performed by BD FACSCalibur™ for four colour analysis and BD FACSCanto™ flow cytometer for eight colour analysis. CD19, CD45, CD38, CD138 and CD56 expression was determined for all patients and for those cases where eight colour analysis was applied, CD27, CD28, CD117 and CD81 expression was studied. All the FCS data was analysed using infinicyt software. Plasma cells were identified by primarily gating on CD38 and CD138 positive cells. Mean fluorescent intensity of CD19 expression on plasma cells was compared with that of B-lymphocytes to determine positive or negative expression. It was considered a positive expression if 20% of the CPCs were positive.
Results
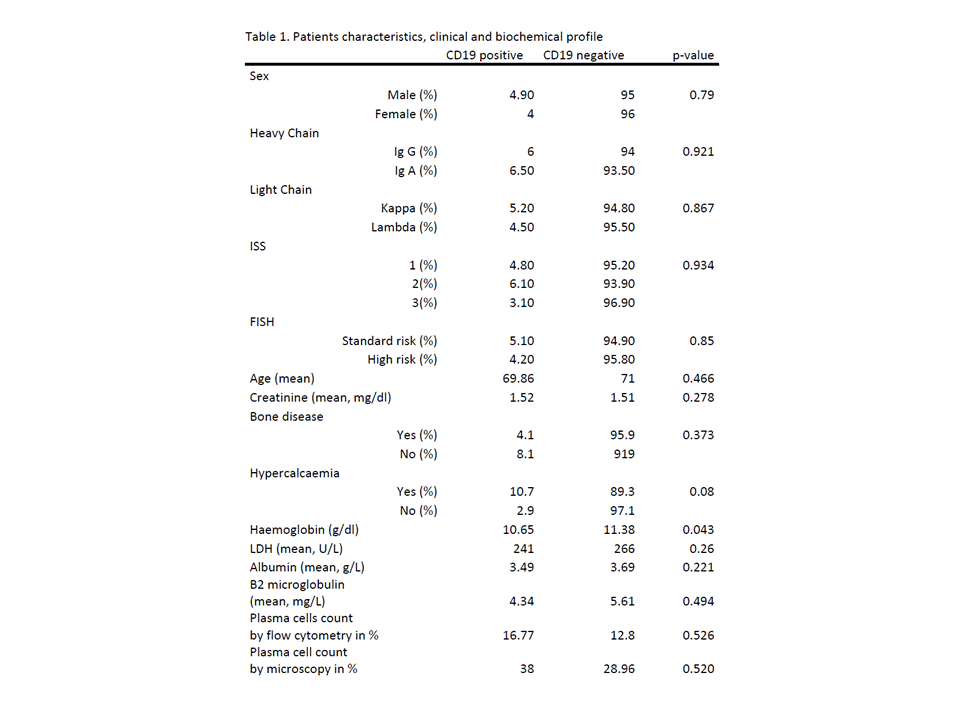
A total of 157 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients were reviewed. The incidence of CD19 positive myeloma cases was 4.46%. Out of 7 patients who were CD19 positive, four patients had homogeneous strong positive expression while the remainder had heterogeneous dim positive expression. Baseline demographics of the patients, ISS, immunoglobulin subtypes and clinical parameters at presentation i.e. related organ and tissue impairment, LDH, albumin,beta2 microglobulin levels and cytogenetic risks were similar in both CD19 positive and CD19 negative myeloma patients (Table 1). CD56 expression was 100% and 74% positive in CD19 positive and negative myeloma patients respectively (P 0.12). There was a higher percentage of positive CD81 expression (80% vs. 37.3%, P 0.056) and higher percentage of negative CD27 expression (60% vs. 35.9%, P 0.276) in CD19 positive cases though it did not reach statistical significance. No statistically significant difference in overall survival was found with a median OS of 56 and 75 months for CD19 positive and negative cases respectively (P 0.847).
Summary
In our study, CD19 expression was associated with a 100% positive CD56 expression, a higher positive CD81 expression and a higher negative CD27 expression rate even though statistical significance was not reached due to few numbers of patients in the cohort. This could be a useful finding for MRD assessment of the patients as well as to differentiate CPCs from PPCs in MGUS or smoldering myeloma by MFC. In the current cohort, we did not demonstrate a poorer prognostic impact of CD19 positive expression. This could be explained by the difference in the treatment era of the study patients where almost all the patients eligible for treatment received one or more novel therapeutic agents, compared to previous cohorts. Prospective studies with larger cohorts may further elucidate the significance of CD19 positive myeloma.
Keyword(s): CD19, Flow cytometry, Multiple myeloma
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Clonal plasma cells (CPCs) in multiple myeloma were usually characterized by negative CD19 expression by multiparametric flow cytometry (MFC). However, positive CD19 expression in CPCs was noted in some cases with the reported incidence ranging from 0 to 8%. Positive CD19 expression in CPCs could complicate the minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment by high sensitivity MFC as the majority of polyclonal plasma cells (PPCs) retained CD19 expression. In addition, CD19 positive myeloma patients were reported to have a poorer clinical outcome in the group of patients treated with induction chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation.
Aims
We aimed to review the immunophenotypic features of CD19 positive myeloma patients in comparison with that of CD19 negative cases to determine specific immunophenotypes which could be useful for MRD assessment. The prognostic impact of positive CD19 expression on clinical outcome in patients treated with the regimens including novel therapies was also evaluated.
Methods
A retrospective review of newly diagnosed myeloma patients in a single centre was performed for the period of Jan 2006 to Jan 2015. The clinical data was retrieved from the patient information system of the institution as well as by reviewing the clinical records. Multiparametric flow cytometry analysis was performed by BD FACSCalibur™ for four colour analysis and BD FACSCanto™ flow cytometer for eight colour analysis. CD19, CD45, CD38, CD138 and CD56 expression was determined for all patients and for those cases where eight colour analysis was applied, CD27, CD28, CD117 and CD81 expression was studied. All the FCS data was analysed using infinicyt software. Plasma cells were identified by primarily gating on CD38 and CD138 positive cells. Mean fluorescent intensity of CD19 expression on plasma cells was compared with that of B-lymphocytes to determine positive or negative expression. It was considered a positive expression if 20% of the CPCs were positive.
Results
A total of 157 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients were reviewed. The incidence of CD19 positive myeloma cases was 4.46%. Out of 7 patients who were CD19 positive, four patients had homogeneous strong positive expression while the remainder had heterogeneous dim positive expression. Baseline demographics of the patients, ISS, immunoglobulin subtypes and clinical parameters at presentation i.e. related organ and tissue impairment, LDH, albumin,beta2 microglobulin levels and cytogenetic risks were similar in both CD19 positive and CD19 negative myeloma patients (Table 1). CD56 expression was 100% and 74% positive in CD19 positive and negative myeloma patients respectively (P 0.12). There was a higher percentage of positive CD81 expression (80% vs. 37.3%, P 0.056) and higher percentage of negative CD27 expression (60% vs. 35.9%, P 0.276) in CD19 positive cases though it did not reach statistical significance. No statistically significant difference in overall survival was found with a median OS of 56 and 75 months for CD19 positive and negative cases respectively (P 0.847).
Summary
In our study, CD19 expression was associated with a 100% positive CD56 expression, a higher positive CD81 expression and a higher negative CD27 expression rate even though statistical significance was not reached due to few numbers of patients in the cohort. This could be a useful finding for MRD assessment of the patients as well as to differentiate CPCs from PPCs in MGUS or smoldering myeloma by MFC. In the current cohort, we did not demonstrate a poorer prognostic impact of CD19 positive expression. This could be explained by the difference in the treatment era of the study patients where almost all the patients eligible for treatment received one or more novel therapeutic agents, compared to previous cohorts. Prospective studies with larger cohorts may further elucidate the significance of CD19 positive myeloma.
Keyword(s): CD19, Flow cytometry, Multiple myeloma

Session topic: Publication Only
Abstract: PB1872
Type: Publication Only
Background
Clonal plasma cells (CPCs) in multiple myeloma were usually characterized by negative CD19 expression by multiparametric flow cytometry (MFC). However, positive CD19 expression in CPCs was noted in some cases with the reported incidence ranging from 0 to 8%. Positive CD19 expression in CPCs could complicate the minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment by high sensitivity MFC as the majority of polyclonal plasma cells (PPCs) retained CD19 expression. In addition, CD19 positive myeloma patients were reported to have a poorer clinical outcome in the group of patients treated with induction chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation.
Aims
We aimed to review the immunophenotypic features of CD19 positive myeloma patients in comparison with that of CD19 negative cases to determine specific immunophenotypes which could be useful for MRD assessment. The prognostic impact of positive CD19 expression on clinical outcome in patients treated with the regimens including novel therapies was also evaluated.
Methods
A retrospective review of newly diagnosed myeloma patients in a single centre was performed for the period of Jan 2006 to Jan 2015. The clinical data was retrieved from the patient information system of the institution as well as by reviewing the clinical records. Multiparametric flow cytometry analysis was performed by BD FACSCalibur™ for four colour analysis and BD FACSCanto™ flow cytometer for eight colour analysis. CD19, CD45, CD38, CD138 and CD56 expression was determined for all patients and for those cases where eight colour analysis was applied, CD27, CD28, CD117 and CD81 expression was studied. All the FCS data was analysed using infinicyt software. Plasma cells were identified by primarily gating on CD38 and CD138 positive cells. Mean fluorescent intensity of CD19 expression on plasma cells was compared with that of B-lymphocytes to determine positive or negative expression. It was considered a positive expression if 20% of the CPCs were positive.
Results
A total of 157 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients were reviewed. The incidence of CD19 positive myeloma cases was 4.46%. Out of 7 patients who were CD19 positive, four patients had homogeneous strong positive expression while the remainder had heterogeneous dim positive expression. Baseline demographics of the patients, ISS, immunoglobulin subtypes and clinical parameters at presentation i.e. related organ and tissue impairment, LDH, albumin,beta2 microglobulin levels and cytogenetic risks were similar in both CD19 positive and CD19 negative myeloma patients (Table 1). CD56 expression was 100% and 74% positive in CD19 positive and negative myeloma patients respectively (P 0.12). There was a higher percentage of positive CD81 expression (80% vs. 37.3%, P 0.056) and higher percentage of negative CD27 expression (60% vs. 35.9%, P 0.276) in CD19 positive cases though it did not reach statistical significance. No statistically significant difference in overall survival was found with a median OS of 56 and 75 months for CD19 positive and negative cases respectively (P 0.847).
Summary
In our study, CD19 expression was associated with a 100% positive CD56 expression, a higher positive CD81 expression and a higher negative CD27 expression rate even though statistical significance was not reached due to few numbers of patients in the cohort. This could be a useful finding for MRD assessment of the patients as well as to differentiate CPCs from PPCs in MGUS or smoldering myeloma by MFC. In the current cohort, we did not demonstrate a poorer prognostic impact of CD19 positive expression. This could be explained by the difference in the treatment era of the study patients where almost all the patients eligible for treatment received one or more novel therapeutic agents, compared to previous cohorts. Prospective studies with larger cohorts may further elucidate the significance of CD19 positive myeloma.
Keyword(s): CD19, Flow cytometry, Multiple myeloma

Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Clonal plasma cells (CPCs) in multiple myeloma were usually characterized by negative CD19 expression by multiparametric flow cytometry (MFC). However, positive CD19 expression in CPCs was noted in some cases with the reported incidence ranging from 0 to 8%. Positive CD19 expression in CPCs could complicate the minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment by high sensitivity MFC as the majority of polyclonal plasma cells (PPCs) retained CD19 expression. In addition, CD19 positive myeloma patients were reported to have a poorer clinical outcome in the group of patients treated with induction chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplantation.
Aims
We aimed to review the immunophenotypic features of CD19 positive myeloma patients in comparison with that of CD19 negative cases to determine specific immunophenotypes which could be useful for MRD assessment. The prognostic impact of positive CD19 expression on clinical outcome in patients treated with the regimens including novel therapies was also evaluated.
Methods
A retrospective review of newly diagnosed myeloma patients in a single centre was performed for the period of Jan 2006 to Jan 2015. The clinical data was retrieved from the patient information system of the institution as well as by reviewing the clinical records. Multiparametric flow cytometry analysis was performed by BD FACSCalibur™ for four colour analysis and BD FACSCanto™ flow cytometer for eight colour analysis. CD19, CD45, CD38, CD138 and CD56 expression was determined for all patients and for those cases where eight colour analysis was applied, CD27, CD28, CD117 and CD81 expression was studied. All the FCS data was analysed using infinicyt software. Plasma cells were identified by primarily gating on CD38 and CD138 positive cells. Mean fluorescent intensity of CD19 expression on plasma cells was compared with that of B-lymphocytes to determine positive or negative expression. It was considered a positive expression if 20% of the CPCs were positive.
Results
A total of 157 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients were reviewed. The incidence of CD19 positive myeloma cases was 4.46%. Out of 7 patients who were CD19 positive, four patients had homogeneous strong positive expression while the remainder had heterogeneous dim positive expression. Baseline demographics of the patients, ISS, immunoglobulin subtypes and clinical parameters at presentation i.e. related organ and tissue impairment, LDH, albumin,beta2 microglobulin levels and cytogenetic risks were similar in both CD19 positive and CD19 negative myeloma patients (Table 1). CD56 expression was 100% and 74% positive in CD19 positive and negative myeloma patients respectively (P 0.12). There was a higher percentage of positive CD81 expression (80% vs. 37.3%, P 0.056) and higher percentage of negative CD27 expression (60% vs. 35.9%, P 0.276) in CD19 positive cases though it did not reach statistical significance. No statistically significant difference in overall survival was found with a median OS of 56 and 75 months for CD19 positive and negative cases respectively (P 0.847).
Summary
In our study, CD19 expression was associated with a 100% positive CD56 expression, a higher positive CD81 expression and a higher negative CD27 expression rate even though statistical significance was not reached due to few numbers of patients in the cohort. This could be a useful finding for MRD assessment of the patients as well as to differentiate CPCs from PPCs in MGUS or smoldering myeloma by MFC. In the current cohort, we did not demonstrate a poorer prognostic impact of CD19 positive expression. This could be explained by the difference in the treatment era of the study patients where almost all the patients eligible for treatment received one or more novel therapeutic agents, compared to previous cohorts. Prospective studies with larger cohorts may further elucidate the significance of CD19 positive myeloma.
Keyword(s): CD19, Flow cytometry, Multiple myeloma

Session topic: Publication Only
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


