Hematology

Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
Expression of Wilms tumor antigen (WT1), which encodes a transcription factor, is significantly increased in tumor cells of the kidney, testes, ovaries, breast and certain hematological malignancies. WT1 is overexpressed in many patients with acute myeloid leukemia and in the absence of more specific molecular markers can be used for monitoring of minimal residual disease. The rate and significance of WT1 overexpression in chronic myeloproliferative diseases (MPDs) currently remains unclear
Aims
The aim of this study was to evaluate the incidence of overexpression of WT1 gene in MPDs.
Methods
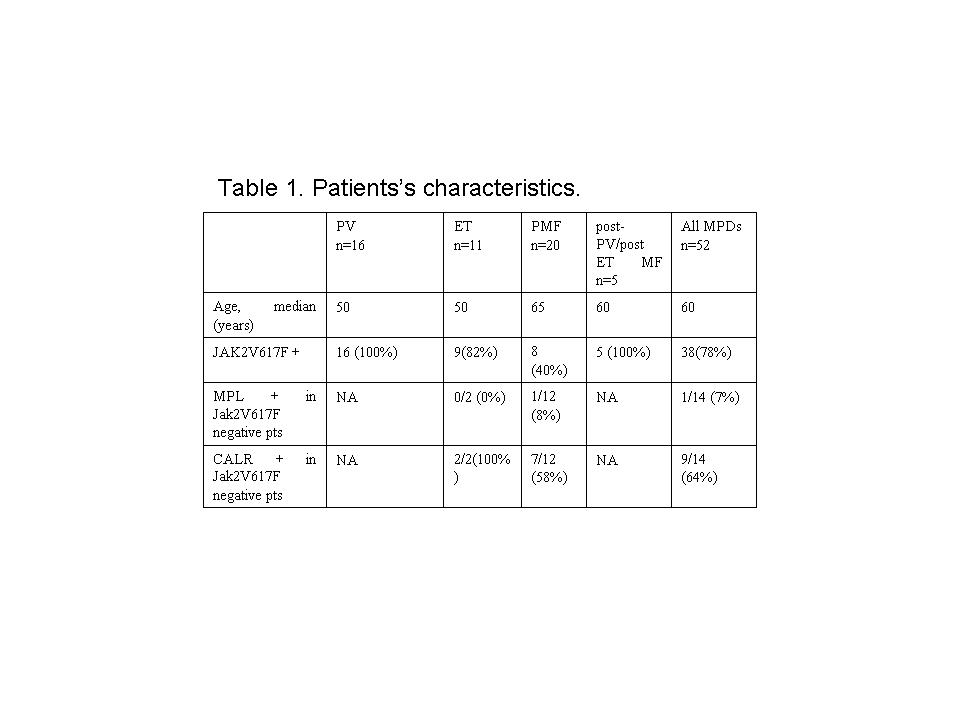
Peripheral blood samples from 52 (male n= 33, female n=19) patients with polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET) and primary or post-PV/post-ET myelofibrosis were evaluated for WT1 expression. Patients’s characteristics at the time of evaluation is presented in the table 1.
WT1 expression was performed by quantitative PCR, using a standard set ProfileQuant Wt1 kit, PCR analyzer «Rotor- Gene 6000'. Normal reference range in peripheral blood considered is 0.00-50.00 WT1/104 ABL copies.
Results
WT1 overexpression was observed in 25/52 (48%) patients. It was found in all patients with myelofibrosis (primary or post-PV/post ET). No patients with PV or ET have WT1 overexpression. The mean level of WT1 gene expression was 714 WT1/104 ABL copies in MF (range, 171-6000), 4.0 WT1/104 ABL copies in PV (range 1.1-17), and 8.32 WT1/104 ABL copies in ET(range, 1.8-14) .
We did not find any significant correlation of WT1 expression level with either mutation status of Jak2, MPL and CALR genes or clinical data (age, gender, DIPSS risk groups, median time from MF diagnosis).
Summary
WT1 gene was overexpressed in all MF, including post-PV/post-ET cases, but was normal in PV and ET patients. It seems that WT1 gene overexpression could be potential marker for prediction of bone marrow fibrosis development in patients with PV/ET. Whether the level of expression of WT1 is correlated to grade of fibrosis is a subject of our investigation.
Keyword(s): Myelofibrosis, Myeloproliferative disorder, Overexpression, WT1
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Expression of Wilms tumor antigen (WT1), which encodes a transcription factor, is significantly increased in tumor cells of the kidney, testes, ovaries, breast and certain hematological malignancies. WT1 is overexpressed in many patients with acute myeloid leukemia and in the absence of more specific molecular markers can be used for monitoring of minimal residual disease. The rate and significance of WT1 overexpression in chronic myeloproliferative diseases (MPDs) currently remains unclear
Aims
The aim of this study was to evaluate the incidence of overexpression of WT1 gene in MPDs.
Methods
Peripheral blood samples from 52 (male n= 33, female n=19) patients with polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET) and primary or post-PV/post-ET myelofibrosis were evaluated for WT1 expression. Patients’s characteristics at the time of evaluation is presented in the table 1.
WT1 expression was performed by quantitative PCR, using a standard set ProfileQuant Wt1 kit, PCR analyzer «Rotor- Gene 6000'. Normal reference range in peripheral blood considered is 0.00-50.00 WT1/104 ABL copies.
Results
WT1 overexpression was observed in 25/52 (48%) patients. It was found in all patients with myelofibrosis (primary or post-PV/post ET). No patients with PV or ET have WT1 overexpression. The mean level of WT1 gene expression was 714 WT1/104 ABL copies in MF (range, 171-6000), 4.0 WT1/104 ABL copies in PV (range 1.1-17), and 8.32 WT1/104 ABL copies in ET(range, 1.8-14) .
We did not find any significant correlation of WT1 expression level with either mutation status of Jak2, MPL and CALR genes or clinical data (age, gender, DIPSS risk groups, median time from MF diagnosis).
Summary
WT1 gene was overexpressed in all MF, including post-PV/post-ET cases, but was normal in PV and ET patients. It seems that WT1 gene overexpression could be potential marker for prediction of bone marrow fibrosis development in patients with PV/ET. Whether the level of expression of WT1 is correlated to grade of fibrosis is a subject of our investigation.
Keyword(s): Myelofibrosis, Myeloproliferative disorder, Overexpression, WT1

Session topic: Publication Only


