hematology department sfax hospital

Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
The acquired aplastic anemia (AAA) is a rare but serious and severe disease. Evolution could be fatal by medullary isuffisance ‘s complications.
Aims
We found it useful to carry out a retrospective study over a period of 16 years and to analyze the diagnostic, therapeutic and evolutive characteristics of myelosuppression in southern Tunisia.
Methods
Our study is retrospective, it has enrolled the acquired aplastic anemia patients diagnosed and monitored in the hematology department of Sfax hospital over 16 years from january 1998 to december 2013. 107 cases were collected.The date of point was fixed to January 2015. The etiological diagnosis contained a careful history, a study of medullary and constitutional karyotype, a search for HPN clone, viral serology … overall survival was carried out according to Kaplan Meier method.
Results
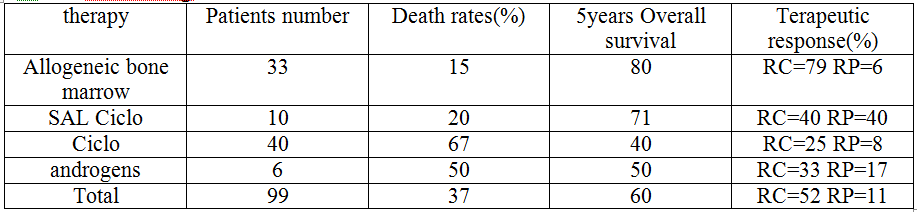
107 cases of acquired aplastic anemia were collected, they were 60 men and 47 women with a median age of 27 years (range 2-81 years). The circumstances of discovery were hemorrhagic syndrome, anemic syndrome and fever respectively in 7%, % and11% of cases. Our patient’s distribution according to Camitta) score showed 38% AAA moderate, 31% severe AAA and 31% very severe AAA. The etiological investigation has revealed negative in 85 patients (79%) and labeled idiopathic. It showed a toxic agents or viral infections as in postseronegative hepatitis respectively in 7% and 11% of patients. Two patients have had AM / HPN .In addition to symptomatic treatment, specific treatment concerned 99 patients. It involved the allogenic bone marrow (allograft), ciclo associated with SAL, ciclo only and androgen.The therapeutic results according to the used therapeutics are detailed in the following table
Summary
The acquired aplastic anemia is a rare and serious disease. It is a therapeutic emergency requiring a carefull etiological investigation and early management with effective therapeutic.
Keyword(s): Allogeneic bone marrow transplant, Aplastic anemia
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
The acquired aplastic anemia (AAA) is a rare but serious and severe disease. Evolution could be fatal by medullary isuffisance ‘s complications.
Aims
We found it useful to carry out a retrospective study over a period of 16 years and to analyze the diagnostic, therapeutic and evolutive characteristics of myelosuppression in southern Tunisia.
Methods
Our study is retrospective, it has enrolled the acquired aplastic anemia patients diagnosed and monitored in the hematology department of Sfax hospital over 16 years from january 1998 to december 2013. 107 cases were collected.The date of point was fixed to January 2015. The etiological diagnosis contained a careful history, a study of medullary and constitutional karyotype, a search for HPN clone, viral serology … overall survival was carried out according to Kaplan Meier method.
Results
107 cases of acquired aplastic anemia were collected, they were 60 men and 47 women with a median age of 27 years (range 2-81 years). The circumstances of discovery were hemorrhagic syndrome, anemic syndrome and fever respectively in 7%, % and11% of cases. Our patient’s distribution according to Camitta) score showed 38% AAA moderate, 31% severe AAA and 31% very severe AAA. The etiological investigation has revealed negative in 85 patients (79%) and labeled idiopathic. It showed a toxic agents or viral infections as in postseronegative hepatitis respectively in 7% and 11% of patients. Two patients have had AM / HPN .In addition to symptomatic treatment, specific treatment concerned 99 patients. It involved the allogenic bone marrow (allograft), ciclo associated with SAL, ciclo only and androgen.The therapeutic results according to the used therapeutics are detailed in the following table
Summary
The acquired aplastic anemia is a rare and serious disease. It is a therapeutic emergency requiring a carefull etiological investigation and early management with effective therapeutic.
Keyword(s): Allogeneic bone marrow transplant, Aplastic anemia

Session topic: Publication Only


