Genetics

Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative disorder of blood stem cells. More than 95% of patients with detected translocation t(9;22) is characterized by the fusion between exons e13 or e14 of BCR gene, which are located in major breakpoint cluster region (M-bcr) and exon a2 of ABL gene. These fusions are described as b2a2 (e13a2) and b3a2 (e14a2). Because patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors achieve lower levels of detectable disease, quantification of BCR-ABL transcripts with quantitative RT-PCR has become an essential tool in chronic myeloid leukemia monitoring. Major molecular response (MMR; i.e., a ≥3-log reduction in BCR-ABL transcript levels) is used in current treatment guidelines to assess prognosis. Recent evidence suggests that deeper molecular responses (≥4-log reductions in BCR-ABL transcript levels), particularly when attained early during treatment, may have even better correlation with long-term outcomes, including survival and disease progression. Therefore, quantitative measurement of BCR-ABL transcripts in blood and bone marrow both aids in the initial diagnosis of CML is essential for routine post-therapy minimal residual disease monitoring. Establishing methods for secure long-term storage of RNA is critical to realize MRD monitoring. We describe the results of RNA stability in the same set for whole blood RNA collecting in Tempus Blood RNA tubes and tubes with EDTA.
Aims
All the steps of the preanalytical phase (blood collection, conservation and procedures of isolation RNA) are influencing on the number of copies of the ABL control gene in the analysis of BCR/ABL transcripts. Our aim was to show the differences in the stability of the RNA using EDTA tubes and tubes with a special stabilizing solution Tempus (TempusTM VACUETTE® Blood RNA Tube) for the collection of peripheral blood and bone marrow in CML.
Methods
Various kits for stabilizing the RNA at the time of blood collection were developed: Ambion RNA later (Applied Biosystems) and the new Tempus Blood RNA kit (Applied Biosystems). The Tempus Blood RNA kit (VACUETTE® TempusTM Blood RNA Tube) uses tubes containing a proprietary blend of reagents based on a patented RNA stabilization technology. In order to evaluate the Tempus Blood RNA kit, it was compared to unstabilized EDTA blood protocol. The RNAs extracted by the different methods were assessed for quantity control gene ( ABL) and fusion gene transcripts BCR-ABL by QRT-PCR. After extraction, both RNA purity were measured by using both, the ratio A260/280, no significant changes in these ratios were observed in either system. The integrity of RNA after extraction was confirmed using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer and was indicated by the RIN.
Results
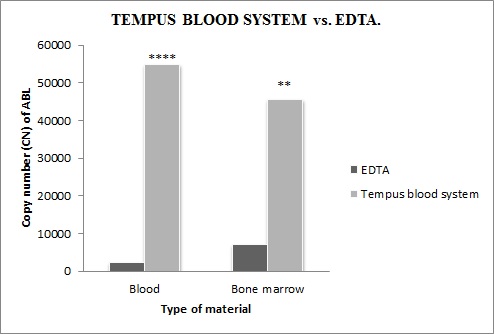
Our results strongly suggest the superiority of the stabilization system special tubes over the unstabilized EDTA blood. Tempus tubes are preventing the degradation of RNA at the time of the preanalytical phase during genetic analysis of CML patients. Using Tempus tubes we have achieved increased stability of RNA, which has a direct impact on increasing the number of copies of the ABL control gene (3-4 times) for the analysis of BCR/ABL and thus ultimately increases the sensitivity of QRT-PCR method. Tempus blood RNA systems have been shown to provide efficient stabilization of the blood RNA for several days at room temperature.
Fig. Comparison of expression levels of ABL control gene in RNA (10 patients) extracted by EDTA or Tempus Blood RNA system. ABL expressions are expressed as copy number. P-value: in blood p<0.0001 and in bone marrow p<0.0101 (t-test).
Summary
In summary, molecular response measured by BCR-ABL QRT-PCR provides important prognostic information for the management of patients with CML treated with TKI therapies. The deeper molecular response (MR4, MR4.5, and MR5) that is necessary to enroll a patient in a trial aiming at treatment-free remission (TFR).
Type: Publication Only
Background
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a myeloproliferative disorder of blood stem cells. More than 95% of patients with detected translocation t(9;22) is characterized by the fusion between exons e13 or e14 of BCR gene, which are located in major breakpoint cluster region (M-bcr) and exon a2 of ABL gene. These fusions are described as b2a2 (e13a2) and b3a2 (e14a2). Because patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors achieve lower levels of detectable disease, quantification of BCR-ABL transcripts with quantitative RT-PCR has become an essential tool in chronic myeloid leukemia monitoring. Major molecular response (MMR; i.e., a ≥3-log reduction in BCR-ABL transcript levels) is used in current treatment guidelines to assess prognosis. Recent evidence suggests that deeper molecular responses (≥4-log reductions in BCR-ABL transcript levels), particularly when attained early during treatment, may have even better correlation with long-term outcomes, including survival and disease progression. Therefore, quantitative measurement of BCR-ABL transcripts in blood and bone marrow both aids in the initial diagnosis of CML is essential for routine post-therapy minimal residual disease monitoring. Establishing methods for secure long-term storage of RNA is critical to realize MRD monitoring. We describe the results of RNA stability in the same set for whole blood RNA collecting in Tempus Blood RNA tubes and tubes with EDTA.
Aims
All the steps of the preanalytical phase (blood collection, conservation and procedures of isolation RNA) are influencing on the number of copies of the ABL control gene in the analysis of BCR/ABL transcripts. Our aim was to show the differences in the stability of the RNA using EDTA tubes and tubes with a special stabilizing solution Tempus (TempusTM VACUETTE® Blood RNA Tube) for the collection of peripheral blood and bone marrow in CML.
Methods
Various kits for stabilizing the RNA at the time of blood collection were developed: Ambion RNA later (Applied Biosystems) and the new Tempus Blood RNA kit (Applied Biosystems). The Tempus Blood RNA kit (VACUETTE® TempusTM Blood RNA Tube) uses tubes containing a proprietary blend of reagents based on a patented RNA stabilization technology. In order to evaluate the Tempus Blood RNA kit, it was compared to unstabilized EDTA blood protocol. The RNAs extracted by the different methods were assessed for quantity control gene ( ABL) and fusion gene transcripts BCR-ABL by QRT-PCR. After extraction, both RNA purity were measured by using both, the ratio A260/280, no significant changes in these ratios were observed in either system. The integrity of RNA after extraction was confirmed using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer and was indicated by the RIN.
Results
Our results strongly suggest the superiority of the stabilization system special tubes over the unstabilized EDTA blood. Tempus tubes are preventing the degradation of RNA at the time of the preanalytical phase during genetic analysis of CML patients. Using Tempus tubes we have achieved increased stability of RNA, which has a direct impact on increasing the number of copies of the ABL control gene (3-4 times) for the analysis of BCR/ABL and thus ultimately increases the sensitivity of QRT-PCR method. Tempus blood RNA systems have been shown to provide efficient stabilization of the blood RNA for several days at room temperature.
Fig. Comparison of expression levels of ABL control gene in RNA (10 patients) extracted by EDTA or Tempus Blood RNA system. ABL expressions are expressed as copy number. P-value: in blood p<0.0001 and in bone marrow p<0.0101 (t-test).
Summary
In summary, molecular response measured by BCR-ABL QRT-PCR provides important prognostic information for the management of patients with CML treated with TKI therapies. The deeper molecular response (MR4, MR4.5, and MR5) that is necessary to enroll a patient in a trial aiming at treatment-free remission (TFR).



