
Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
The associations between the Arg399Gln polymorphism in X-ray repair cross-complementing gene 1 (XRCC1) gene and the risk of hematological malignancies have been extensively investigated. In the subgroup analysis by ethnicity and cancer types, significant association was found in Asians but not in Europeans (Du L e.a. 2015 PMID: 25619474). No data on any it association with Ph-negative myeloid neoplasms.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the association between XRCC1 Arg399Gln and Ph-negative myeloid neoplasms risk in patients of the Krasnoyarsk Territory.
Methods
In this study was included 134 cases with ET -75 V617F JAK2 (+), 31 CALR(+) and 5 MPL(+), 91 patients was included with PV -79 V617F JAK2(+). The control group (n= 114) consisted of healthy individuals. The XRCC1 polymorphism was detected in DNA isolated from peripheral leucocytes using PCR-based Taqman assay using a 'iQ iCycler' 5.0. We used two pairs of primers (F: GTA-AGG-AGT-GGG-TGC-TGG-ACT-GT; R: GTC-TGA-CTC-CCC-TCC-AGA-TTC-C) and two probes (A allele: FAM-CTG-CCC-TCC-CAG-AGG-TAA-GGC-CTC-BHQ1; G allele: HEX-CTG-CCC-TCC-CGG-AGG-TAA-GGC-C-BHQ1).
Results
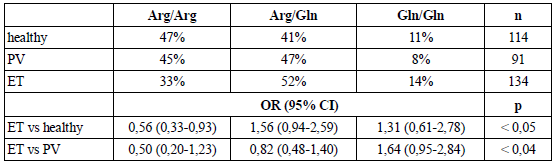
Our data are shown in the table. The additive model of Arg399Gln was associated with Essential Thrombocytemia (ET) risk. Conversely, no statistical association was found with Polycythemia vera (PV).
Summary
The differences were found in the association between the polymorphism PV and ET to suggest Arg allele of the Arg399Gln polymorphism prevents the loss of homozygosity typical to PV.
Keyword(s): Essential Thrombocytemia, Mutation analysis, Myelofibrosis, Polycythemia vera
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
The associations between the Arg399Gln polymorphism in X-ray repair cross-complementing gene 1 (XRCC1) gene and the risk of hematological malignancies have been extensively investigated. In the subgroup analysis by ethnicity and cancer types, significant association was found in Asians but not in Europeans (Du L e.a. 2015 PMID: 25619474). No data on any it association with Ph-negative myeloid neoplasms.
Aims
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the association between XRCC1 Arg399Gln and Ph-negative myeloid neoplasms risk in patients of the Krasnoyarsk Territory.
Methods
In this study was included 134 cases with ET -75 V617F JAK2 (+), 31 CALR(+) and 5 MPL(+), 91 patients was included with PV -79 V617F JAK2(+). The control group (n= 114) consisted of healthy individuals. The XRCC1 polymorphism was detected in DNA isolated from peripheral leucocytes using PCR-based Taqman assay using a 'iQ iCycler' 5.0. We used two pairs of primers (F: GTA-AGG-AGT-GGG-TGC-TGG-ACT-GT; R: GTC-TGA-CTC-CCC-TCC-AGA-TTC-C) and two probes (A allele: FAM-CTG-CCC-TCC-CAG-AGG-TAA-GGC-CTC-BHQ1; G allele: HEX-CTG-CCC-TCC-CGG-AGG-TAA-GGC-C-BHQ1).
Results
Our data are shown in the table. The additive model of Arg399Gln was associated with Essential Thrombocytemia (ET) risk. Conversely, no statistical association was found with Polycythemia vera (PV).
Summary
The differences were found in the association between the polymorphism PV and ET to suggest Arg allele of the Arg399Gln polymorphism prevents the loss of homozygosity typical to PV.
Keyword(s): Essential Thrombocytemia, Mutation analysis, Myelofibrosis, Polycythemia vera

Session topic: Publication Only


