
Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
The introduction of proteasome inhibitors (PIs) and immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) has improved survival of patients (pts) with R/R MM. However, there is little real-world data on PI, IMiD, and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) use.
Aims
The aim of this study was to describe recent US multiple myeloma treatment patterns through August 2014.
Methods
Pts with R/R MM were selected from a longitudinal, nationally-representative electronic medical record (EMR) database (Flatiron Health). MM diagnoses were confirmed by physician (MD) notes. Pts were required to progress after 1st line (1L), ≥ 1 visit after 2010, and ≥ 3 months follow-up post-progression. Data were integrated from structured and unstructured EMR sources: disease class from laboratory results and confirmed in MD notes and ASCT status from MD notes.
Results
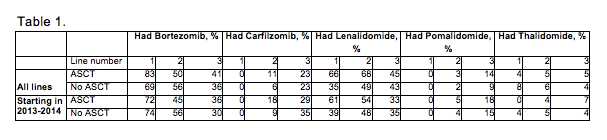
We identified 607 pts with R/R MM (median age, 70 years; 32% < 65 years). Most pts were male (57%), Caucasian (63%), and had IgG myeloma (66%). Of the 117 pts who received an ASCT, the most common 1L regimens were RVD 44%, VD 14%, RD 11%, and CyBorD 9%. In non-ASCT pts, the most common 1L regimens were VD 27%, RVD 16%, RD 14%, and CyBorD 7%. Overall, 29% of pts received both mechanisms of action (MOAs; PIs and IMiDs) in 1L. Of pts exposed to either a PI or IMiD in 1L who went on to receive 2L, 62% switched from PI to IMiD or IMiD to PI, and 30% continued with the same MOA. MOA switching was highest in ASCT pts who received 1L PI (73% received an IMiD in 2L, 23% continued on PI). By 3L, 79% of non-ASCT pts had been exposed to both MOAs vs. 96% in ASCT pts. Treatment utilization is shown in Table 1.
Summary
PIs and IMiDs are the most prevalent MOAs used in R/R MM in the US. Most patients receiving a single MOA in 1L go on to receive the other MOA in 2L, suggesting a perceived clinical benefit of switching MOA. Most patients have been exposed to both MOAs by 2L (67%) or 3L (83%), suggesting a possible need for treatment options with novel MOAs.
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
The introduction of proteasome inhibitors (PIs) and immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) has improved survival of patients (pts) with R/R MM. However, there is little real-world data on PI, IMiD, and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) use.
Aims
The aim of this study was to describe recent US multiple myeloma treatment patterns through August 2014.
Methods
Pts with R/R MM were selected from a longitudinal, nationally-representative electronic medical record (EMR) database (Flatiron Health). MM diagnoses were confirmed by physician (MD) notes. Pts were required to progress after 1st line (1L), ≥ 1 visit after 2010, and ≥ 3 months follow-up post-progression. Data were integrated from structured and unstructured EMR sources: disease class from laboratory results and confirmed in MD notes and ASCT status from MD notes.
Results
We identified 607 pts with R/R MM (median age, 70 years; 32% < 65 years). Most pts were male (57%), Caucasian (63%), and had IgG myeloma (66%). Of the 117 pts who received an ASCT, the most common 1L regimens were RVD 44%, VD 14%, RD 11%, and CyBorD 9%. In non-ASCT pts, the most common 1L regimens were VD 27%, RVD 16%, RD 14%, and CyBorD 7%. Overall, 29% of pts received both mechanisms of action (MOAs; PIs and IMiDs) in 1L. Of pts exposed to either a PI or IMiD in 1L who went on to receive 2L, 62% switched from PI to IMiD or IMiD to PI, and 30% continued with the same MOA. MOA switching was highest in ASCT pts who received 1L PI (73% received an IMiD in 2L, 23% continued on PI). By 3L, 79% of non-ASCT pts had been exposed to both MOAs vs. 96% in ASCT pts. Treatment utilization is shown in Table 1.
Summary
PIs and IMiDs are the most prevalent MOAs used in R/R MM in the US. Most patients receiving a single MOA in 1L go on to receive the other MOA in 2L, suggesting a perceived clinical benefit of switching MOA. Most patients have been exposed to both MOAs by 2L (67%) or 3L (83%), suggesting a possible need for treatment options with novel MOAs.

Session topic: Publication Only


