Haematology

Contributions
Type: Publication Only
Background
ET is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm, characterised by the presence of thrombohemorrhagic events (THE), the evolution to myelofibrosis and acute myeloid leukemia. The mutation of JAK2 exon 14 V617F is detected in 70 % of the patients, and it is related to more THE and a higher number of leukocytes and platelets.
Aims
To analyze the thrombotic (T) and bleeding (B) clinical and analytical profile in patients with ET.
Methods
Clinical files of a sample of patients diagnosed of ET from 1990 to 2014 in our hospital, and that were evaluated in our center consultations for 12 months were reviewed. Demographic and analytical variables, type and THE's location, and the treatment received were analyzed.
Results
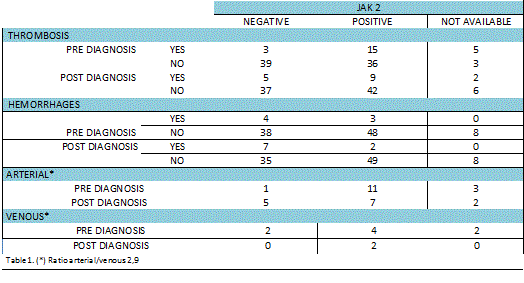
101 patients were valued, 34 ? (33.7 %) and 67 ? (66.3%). Mean age at diagnosis 59.32 (? 56.53 and ? 60.73). A higher prevalence of male (38.2% vs 19.4%) was observed in patients between 45 and 65 years, in contrast to the group of ≥65 years where prevalence in women was higher (65,7% vs 52,9%). 39 events T in 35 patients, 29 arterial (74.3%) and 10 venous (25.7%) which is shown in the data table. T pre diagnosis: 6 in legs, 10 brain, 5 coronary, 1 thrombosis in lower cava, 1 central retinal vein, 78 without thrombosis. Post-diagnosis: 1 in legs, 5 brain, 9 coronary, 1 thrombosis in lower cava, 85 without thrombosis. 51 patients (50.5%) were JAK2 positive (+) and 24 of those presented T (61.5% of the total T), with regard to 7 in group JAK2 negative (-) (results were not available in 8 patients). 16 T (41.02%) were observed during the evolution of disease in 12 patients (11.9%), 4 of these patients didn´t received cytorreductive treatment, 14 antiplatelet therapy and 2 anticoagulantion. B was observed in 16 patients (5 JAK2 +/11 JAK2 -) mainly located in ORL mucous membranes and genitourinary. At diagnosis no significant differences were observed between hematologic values and development of T, however, patients who had developed B events had a higher platelet counts (>900 x 109/L).
Summary
THE define the natural evolution of ET. B events, as shown in literature, are more frequent on mucous membranes levels and in patients with higher platelet counts. We observe a higher frequency of these events in patients JAK2-. A third of the patients developed T events in our series reaching values around 50% in JAK2+, with an incidence of arterial T similar to prospective studies. Despite antithrombotic prophylactic treatment after diagnosis and during the evolution of the disease, 10% of the patients developed T which suggests that a better stratification and control the T risk is needed.
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
ET is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm, characterised by the presence of thrombohemorrhagic events (THE), the evolution to myelofibrosis and acute myeloid leukemia. The mutation of JAK2 exon 14 V617F is detected in 70 % of the patients, and it is related to more THE and a higher number of leukocytes and platelets.
Aims
To analyze the thrombotic (T) and bleeding (B) clinical and analytical profile in patients with ET.
Methods
Clinical files of a sample of patients diagnosed of ET from 1990 to 2014 in our hospital, and that were evaluated in our center consultations for 12 months were reviewed. Demographic and analytical variables, type and THE's location, and the treatment received were analyzed.
Results
101 patients were valued, 34 ? (33.7 %) and 67 ? (66.3%). Mean age at diagnosis 59.32 (? 56.53 and ? 60.73). A higher prevalence of male (38.2% vs 19.4%) was observed in patients between 45 and 65 years, in contrast to the group of ≥65 years where prevalence in women was higher (65,7% vs 52,9%). 39 events T in 35 patients, 29 arterial (74.3%) and 10 venous (25.7%) which is shown in the data table. T pre diagnosis: 6 in legs, 10 brain, 5 coronary, 1 thrombosis in lower cava, 1 central retinal vein, 78 without thrombosis. Post-diagnosis: 1 in legs, 5 brain, 9 coronary, 1 thrombosis in lower cava, 85 without thrombosis. 51 patients (50.5%) were JAK2 positive (+) and 24 of those presented T (61.5% of the total T), with regard to 7 in group JAK2 negative (-) (results were not available in 8 patients). 16 T (41.02%) were observed during the evolution of disease in 12 patients (11.9%), 4 of these patients didn´t received cytorreductive treatment, 14 antiplatelet therapy and 2 anticoagulantion. B was observed in 16 patients (5 JAK2 +/11 JAK2 -) mainly located in ORL mucous membranes and genitourinary. At diagnosis no significant differences were observed between hematologic values and development of T, however, patients who had developed B events had a higher platelet counts (>900 x 109/L).
Summary
THE define the natural evolution of ET. B events, as shown in literature, are more frequent on mucous membranes levels and in patients with higher platelet counts. We observe a higher frequency of these events in patients JAK2-. A third of the patients developed T events in our series reaching values around 50% in JAK2+, with an incidence of arterial T similar to prospective studies. Despite antithrombotic prophylactic treatment after diagnosis and during the evolution of the disease, 10% of the patients developed T which suggests that a better stratification and control the T risk is needed.

Session topic: Publication Only


