SUBCUTANEOUS PANNICULITIS-LIKE T-CELL LYMPHOMA: CLINICAL CHARACTERISTICS AND SURVIVAL STUDY OF 21 THAI PATIENTS IN A SINGLE INSTITUTION
(Abstract release date: 05/21/15)
EHA Library. Julamanee J. 06/12/15; 102699; PB1661
Disclosure(s): Prince of Songkla UniversityDepartment of Internal Medicine

Dr. Jakrawadee Julamanee
Contributions
Contributions
Abstract
Abstract: PB1661
Type: Publication Only
Background
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) is a rare lymphoma subtype which is commonly associated with hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS) and had an aggressive clinical course. The incidence of SPTCL is high in Asian countries including Thailand. Due to the rarity of the disease, there are limited data on the clinical characteristics and optimal therapeutic approaches of this entity.
Aims
The aim of this study was to characterize the clinical features, treatment outcomes, and survival of SPTCL in Thai patients at a single institution.
Methods
Twenty-one patients diagnosed as SPTCL according to WHO classification 2008 were enrolled from January 2001 to December 2014 in Songklanagarind Hospital. All tissue specimens were reviewed by hematopathologist. The demographic, clinical, treatment, and outcomes data were collected for analyses.
Results
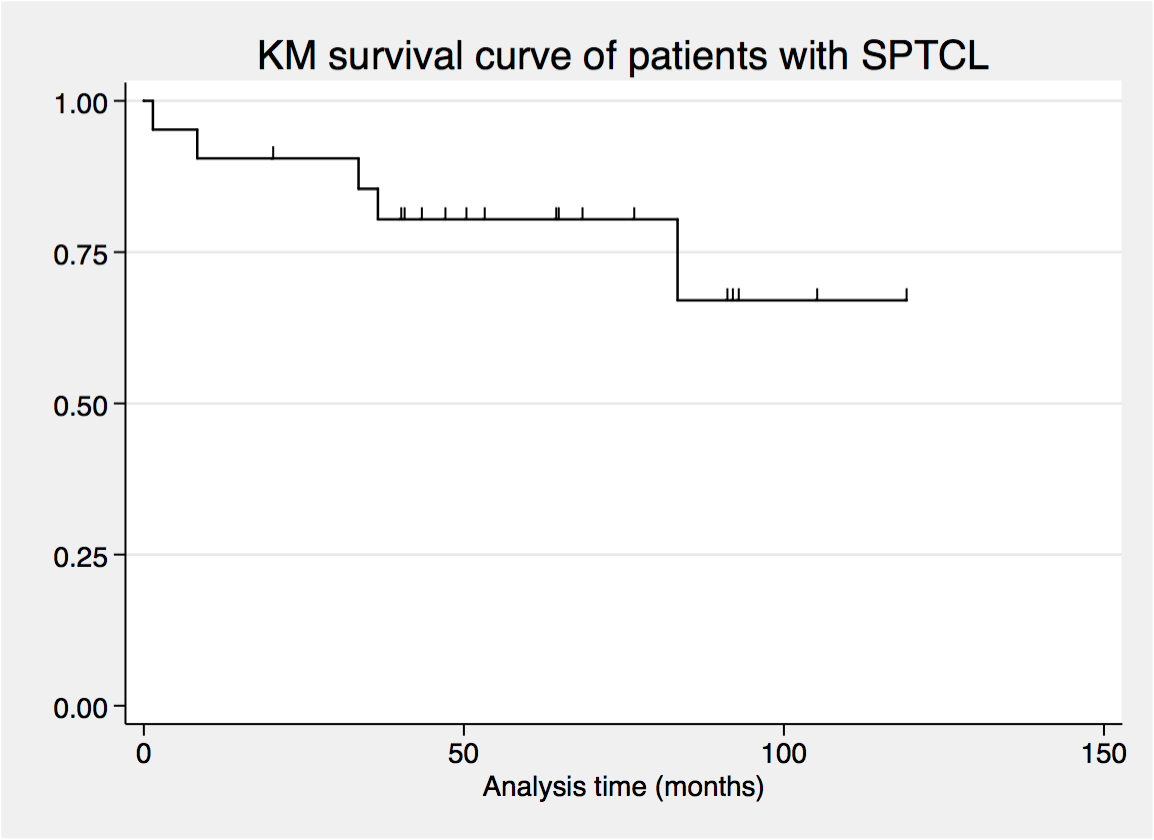
The median age was 33 years (range 22-64 years) and 12 patients were female. Lesions usually presented as multifocal subcutaneous nodules or masses in 90%, commonly at lower extremities and trunk. Nine patients had extra-cutaneous manifestations. The common sites of involvement were liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. None of the patients had HPS in this study. Most patients had a good ECOG performance score (90%) and low prognostic scores (IPI low to low-intermediate in 71% and PIT score 0-1 in 90%). Fifty-seven percent of the patients had limited stage of disease. B symptoms occurred in 57% and elevated LDH level in 86%. Nineteen (90%) patients were treated with chemotherapy, CHOP chemotherapy was used in 85%. Only one patient was treated with radiotherapy. Of the 20 patients evaluated, the overall response rate was 85% with 75% complete remission. Nevertheless, progressive disease occurred in 8 patients, including 5 patients who had obtained complete remission. With median follow-up time of 52 months, the median OS and RFS were unreached. The 5-year OS and RFS were 80% and 68%, respectively. No significant prognostic factors were identified in this study.
Summary
SPTCL frequently affected young females. Lesions typically presented as multifocal subcutaneous nodules or masses on trunk and lower extremities. Patients responded well to CHOP chemotherapy with long-term survival outcomes.
Keyword(s): Clinical data, Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, Survival
Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) is a rare lymphoma subtype which is commonly associated with hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS) and had an aggressive clinical course. The incidence of SPTCL is high in Asian countries including Thailand. Due to the rarity of the disease, there are limited data on the clinical characteristics and optimal therapeutic approaches of this entity.
Aims
The aim of this study was to characterize the clinical features, treatment outcomes, and survival of SPTCL in Thai patients at a single institution.
Methods
Twenty-one patients diagnosed as SPTCL according to WHO classification 2008 were enrolled from January 2001 to December 2014 in Songklanagarind Hospital. All tissue specimens were reviewed by hematopathologist. The demographic, clinical, treatment, and outcomes data were collected for analyses.
Results
The median age was 33 years (range 22-64 years) and 12 patients were female. Lesions usually presented as multifocal subcutaneous nodules or masses in 90%, commonly at lower extremities and trunk. Nine patients had extra-cutaneous manifestations. The common sites of involvement were liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. None of the patients had HPS in this study. Most patients had a good ECOG performance score (90%) and low prognostic scores (IPI low to low-intermediate in 71% and PIT score 0-1 in 90%). Fifty-seven percent of the patients had limited stage of disease. B symptoms occurred in 57% and elevated LDH level in 86%. Nineteen (90%) patients were treated with chemotherapy, CHOP chemotherapy was used in 85%. Only one patient was treated with radiotherapy. Of the 20 patients evaluated, the overall response rate was 85% with 75% complete remission. Nevertheless, progressive disease occurred in 8 patients, including 5 patients who had obtained complete remission. With median follow-up time of 52 months, the median OS and RFS were unreached. The 5-year OS and RFS were 80% and 68%, respectively. No significant prognostic factors were identified in this study.
Summary
SPTCL frequently affected young females. Lesions typically presented as multifocal subcutaneous nodules or masses on trunk and lower extremities. Patients responded well to CHOP chemotherapy with long-term survival outcomes.
Keyword(s): Clinical data, Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, Survival

Session topic: Publication Only
Abstract: PB1661
Type: Publication Only
Background
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) is a rare lymphoma subtype which is commonly associated with hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS) and had an aggressive clinical course. The incidence of SPTCL is high in Asian countries including Thailand. Due to the rarity of the disease, there are limited data on the clinical characteristics and optimal therapeutic approaches of this entity.
Aims
The aim of this study was to characterize the clinical features, treatment outcomes, and survival of SPTCL in Thai patients at a single institution.
Methods
Twenty-one patients diagnosed as SPTCL according to WHO classification 2008 were enrolled from January 2001 to December 2014 in Songklanagarind Hospital. All tissue specimens were reviewed by hematopathologist. The demographic, clinical, treatment, and outcomes data were collected for analyses.
Results
The median age was 33 years (range 22-64 years) and 12 patients were female. Lesions usually presented as multifocal subcutaneous nodules or masses in 90%, commonly at lower extremities and trunk. Nine patients had extra-cutaneous manifestations. The common sites of involvement were liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. None of the patients had HPS in this study. Most patients had a good ECOG performance score (90%) and low prognostic scores (IPI low to low-intermediate in 71% and PIT score 0-1 in 90%). Fifty-seven percent of the patients had limited stage of disease. B symptoms occurred in 57% and elevated LDH level in 86%. Nineteen (90%) patients were treated with chemotherapy, CHOP chemotherapy was used in 85%. Only one patient was treated with radiotherapy. Of the 20 patients evaluated, the overall response rate was 85% with 75% complete remission. Nevertheless, progressive disease occurred in 8 patients, including 5 patients who had obtained complete remission. With median follow-up time of 52 months, the median OS and RFS were unreached. The 5-year OS and RFS were 80% and 68%, respectively. No significant prognostic factors were identified in this study.
Summary
SPTCL frequently affected young females. Lesions typically presented as multifocal subcutaneous nodules or masses on trunk and lower extremities. Patients responded well to CHOP chemotherapy with long-term survival outcomes.
Keyword(s): Clinical data, Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, Survival

Session topic: Publication Only
Type: Publication Only
Background
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) is a rare lymphoma subtype which is commonly associated with hemophagocytic syndrome (HPS) and had an aggressive clinical course. The incidence of SPTCL is high in Asian countries including Thailand. Due to the rarity of the disease, there are limited data on the clinical characteristics and optimal therapeutic approaches of this entity.
Aims
The aim of this study was to characterize the clinical features, treatment outcomes, and survival of SPTCL in Thai patients at a single institution.
Methods
Twenty-one patients diagnosed as SPTCL according to WHO classification 2008 were enrolled from January 2001 to December 2014 in Songklanagarind Hospital. All tissue specimens were reviewed by hematopathologist. The demographic, clinical, treatment, and outcomes data were collected for analyses.
Results
The median age was 33 years (range 22-64 years) and 12 patients were female. Lesions usually presented as multifocal subcutaneous nodules or masses in 90%, commonly at lower extremities and trunk. Nine patients had extra-cutaneous manifestations. The common sites of involvement were liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. None of the patients had HPS in this study. Most patients had a good ECOG performance score (90%) and low prognostic scores (IPI low to low-intermediate in 71% and PIT score 0-1 in 90%). Fifty-seven percent of the patients had limited stage of disease. B symptoms occurred in 57% and elevated LDH level in 86%. Nineteen (90%) patients were treated with chemotherapy, CHOP chemotherapy was used in 85%. Only one patient was treated with radiotherapy. Of the 20 patients evaluated, the overall response rate was 85% with 75% complete remission. Nevertheless, progressive disease occurred in 8 patients, including 5 patients who had obtained complete remission. With median follow-up time of 52 months, the median OS and RFS were unreached. The 5-year OS and RFS were 80% and 68%, respectively. No significant prognostic factors were identified in this study.
Summary
SPTCL frequently affected young females. Lesions typically presented as multifocal subcutaneous nodules or masses on trunk and lower extremities. Patients responded well to CHOP chemotherapy with long-term survival outcomes.
Keyword(s): Clinical data, Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, Survival

Session topic: Publication Only
{{ help_message }}
{{filter}}


