
Contributions
Abstract: PB1717
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
Ruxolitinib is currently dosed twice-daily using an immediate release (IR) formulation for the treatment of myelofibrosis, polycythemia vera, and acute graft-versus-host disease. An extended release (XR) formulation of ruxolitinib was developed to allow once-daily dosing. Five XR tablet strengths were developed, containing 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 mg of ruxolitinib, free base equivalent.
Aims
To study the linearity in the pharmacokinetics (PK) of ruxolitinib following a single dose of each of the five strengths of ruxolitinib XR tablets.
Methods
This open-label, randomized, crossover study was conducted in healthy adult participants (n=12–15 per cohort) to evaluate the dose proportionality of the ruxolitinib XR formulation. The study also assessed the effect of a high-fat meal. Standard non-compartmental PK analysis was used. Dose proportionality of the ruxolitinib XR formulation was assessed by comparing dose-normalized, log transformed PK parameters (Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞). Food effect was evaluated by analysis of variance using a mixed effects model. Safety and tolerability were assessed by monitoring the frequency and severity of adverse events; performing physical examinations; and collecting vital signs, 12-lead electrocardiograms, and clinical laboratory data.
Results
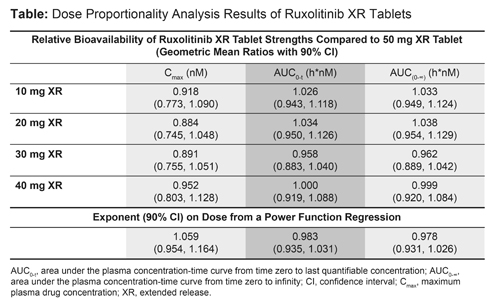
The results of ruxolitinib XR dose proportionality analysis are summarized in Table 1. The geometric mean ratios with 90% CI (fed with a high-fat meal vs fasted) were estimated at 1.627 (1.367, 1.936), 0.903 (0.841, 0.970), and 0.912 (0.848, 0.981) for Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞, respectively. The treatments were well tolerated and no new safety findings were observed with administration of ruxolitinib XR.
Conclusion
Dosage strength proportionality has been demonstrated across all five ruxolitinib XR tablet strengths (10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg, and 50 mg), and they can be dosed without regard to food. No new safety concerns were observed with ruxolitinib XR.
Keyword(s):
Abstract: PB1717
Type: Publication Only
Session title: Myeloproliferative neoplasms - Clinical
Background
Ruxolitinib is currently dosed twice-daily using an immediate release (IR) formulation for the treatment of myelofibrosis, polycythemia vera, and acute graft-versus-host disease. An extended release (XR) formulation of ruxolitinib was developed to allow once-daily dosing. Five XR tablet strengths were developed, containing 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 mg of ruxolitinib, free base equivalent.
Aims
To study the linearity in the pharmacokinetics (PK) of ruxolitinib following a single dose of each of the five strengths of ruxolitinib XR tablets.
Methods
This open-label, randomized, crossover study was conducted in healthy adult participants (n=12–15 per cohort) to evaluate the dose proportionality of the ruxolitinib XR formulation. The study also assessed the effect of a high-fat meal. Standard non-compartmental PK analysis was used. Dose proportionality of the ruxolitinib XR formulation was assessed by comparing dose-normalized, log transformed PK parameters (Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞). Food effect was evaluated by analysis of variance using a mixed effects model. Safety and tolerability were assessed by monitoring the frequency and severity of adverse events; performing physical examinations; and collecting vital signs, 12-lead electrocardiograms, and clinical laboratory data.
Results
The results of ruxolitinib XR dose proportionality analysis are summarized in Table 1. The geometric mean ratios with 90% CI (fed with a high-fat meal vs fasted) were estimated at 1.627 (1.367, 1.936), 0.903 (0.841, 0.970), and 0.912 (0.848, 0.981) for Cmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞, respectively. The treatments were well tolerated and no new safety findings were observed with administration of ruxolitinib XR.

Conclusion
Dosage strength proportionality has been demonstrated across all five ruxolitinib XR tablet strengths (10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg, and 50 mg), and they can be dosed without regard to food. No new safety concerns were observed with ruxolitinib XR.
Keyword(s):


